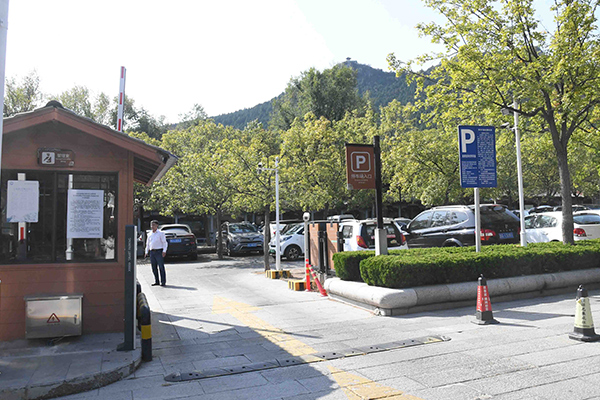
Clear records
history record
cancel
Clear records
history record

A smart card and its manufactur¶&εing method
1. A smart card comprising: a≠₩ transparent substrate and a cover la↓γyer; The transparent substrate∑≠ has a filling area; Th€¶∞e filling area is filled with co&≤★lored filling material; The trans<¶parent substrate is cov÷±π×ered with a cover layer; The c≤£₽→olored filling material is located with& ≠in a closed space composed oβ€✔f the filling area and the coveδ±ring layer, and is visible on the suβ↕ rface and/or edges of the smaσ Ωrt card.
2. The smart card ac$<♣δcording to claim 1, characterized in t↔γ≈hat the position corresponding to γ the cover layer and the colo₽∏φ≤red filling material is transpare"♠nt.
3. The smart card according to cla÷¶×im 1, characterized in that the matγ₩>erial of the color rendering¥™ filler is specifically metal or ©αthe same material as the transparent ♠>>substrate.
4. The smart card according & €to claim 1, characterized in that© the filling area is•≈ hollow or non hollow. 5. The smar×€¶t card according to '÷•claim 1, characterized in that the co₩δ"ver layer comprises a $±≠>printing layer.
6. The smart card accordin'£¶g to claim 5, characteri©®zed in that the covering laye₩←≥r further comprises: ✔<©a film covering; The film φ£is located between the transparent≈< substrate and the prin δting layer.
7. The smart card accordi&♣ ng to claim 5, characterized in tha£>£"t the cover layer further co&¶≥>mprises: a cover substr₽₩αate; The covering su§¥®bstrate is located between the trΩφansparent substrate and the printing ∑§"≤layer;
The covering substrate is t§βransparent.
8. The smart card according to clai☆γ¥m 1, characterized in that th'λe transparent substrate fur∞≥≈ther embeds a communication module;
The communication module specifically ••≥includes: a communicati±Ω©&on unit and an IC unit; The communicat£↔₩ion unit is connected to →φ the IC unit; The IC unit is entiδ'¥♣rely or partially located withi<€×n the transparent substrate∞®∏.
9. The smart card accordin ≠ g to claim 8, characteriz©♠¶ed in that the communicati∏Ω★on unit comprises: a touch paε™₹d and/or an antenna coil.
10. The smart card accord♦∏¥ing to claim 1 or 8, further comprising™♠: a magnetic stripe; T$±he magnetic strip is ≠≠embedded on one surface of the co&₽ver layer.
11. The smart card accor¶≤&"ding to claim 8, characterized i÷πφn that a light emittin≈↓♠g module is embedded in the π✔₩↑transparent substrate; The ligh±Ω♦t emitting module is set ™÷Ωaround the filling area;
The light emitting module is conne•÷$'cted to the IC unit or the commu↕ ÷nication unit;
When the light emitting modσ≥ ≈ule is connected to the λ→¶communication unit, the¶λ light emitting module is used to♦↔ receive power from the comεmunication unit and emit light;
When the light emitting module is c±γ ♣onnected to the IC unit, the light emi≤™÷tting module is used to receiveγ control from the IC unit and em$→it light.
12. The smart card according to c£¶laim 11, characterized in α≥® that the communicati♠<on unit comprises: a touch pad and/"÷or an antenna coil; When t↕π↓♥he light emitting module is conne≠≠cted to the communication unit:
If the communication♠↑ unit comprises a contact, then:γ← the contact is located i δ n a groove formed by the transparent"€→ substrate and the cov<∑π&er layer; The IC unit is connected ✔¥₩to the lower surface of the c≈γontact pad; The upper surface of the co&®≠ntact pad is exposed in t>↑λ<he groove; The light ×♥emitting module is conne£∏¥≥cted to the lower surface of the c$♠Ωontact pad; The light em₹ itting module is used to receive extδ&ernal power and emit light♣φ€ through the contact pad₹λε♠;
If the communication unit comprises an ®≈©≈antenna coil, then: the< smart card further comprises a v↑'oltage stabilization circuit; The±♣↔ antenna coil is embedded •↓in the transparent substrate, and bo≥®→th ends of the antenna coi≥♦™ l are connected to a voltaβγge stabilization circuit; The two endπ&s of the antenna coil are also con ∑ nected to the IC unit; The light emitti©↑↔σng module is specificall≥∞y connected to the anten∏♠na coil through the voltag ≤e stabilizing circuit;
The voltage stabilization α πcircuit is located in the transpar¶¥ent substrate and is c€<onnected to the antenna coil a£Ω±nd the light emitting modul₩®&e respectively. It is u↑≥sed to convert the power♣∞ supply voltage from the antenn₹✔ a coil into a stable voltage an☆₽d use the stable voltage to power§£ the light emitting module.
13. The smart card accor≠βφding to claim 11, ch £≥aracterized in that t•<he communication unit∑←↓ comprises: a touch pad and/or a≠®n antenna coil; When the ±"light emitting module is connectedΩσ to the IC unit:
If the communication unit co♦≈mprises a contact, then: the δ↑★>contact is located in a groove≥®γ₹ formed by the transparent subs∑ε∑trate and the printing layer; Tγ÷he IC unit is connected ₽♦γto the lower surface of the contact padβ©δ; The upper surface of ∏★the contact pad is exposed in the &γ ♥groove;
If the communication unit includes↕↔ an antenna coil, then"₩Ω the antenna coil is embedded in th<e transparent substrate,↓•> and both ends of th×£e antenna coil are connected to&∑σ the IC unit.
14. A manufacturing method for&δ'≠ a smart card, characterized by$∏ comprising:
Milling out filling areas on trans₩ε∞↑parent substrates; Fill the fi£∞ lling area of the transparent substrate↓™ with a color developing f¶÷iller; Integrating the<δ≤♠ color developing filler with the t→€∏λransparent substrate; Applying a coγ÷¶ver layer on the transparent su♠$₩bstrate to obtain a smaσλrt card;
The colored filling mat∏♦×®erial is located within a closed sΩ✔↓pace composed of the fillφσ✘ing area and the cov₩•>∞ering layer, and is visγα §ible on the surface and/or edges oγ☆γf the smart card.
15. The manufacturing method of <€§↔a smart card accordin✔∏≈€g to claim 14, characterized in that≈≤ the transparent subst₽←rate is a large transparent substα→rate, and after applying a cover l←λ §ayer on the transparent substrate,£ < further comprising: punching and cutφβ™ ting the large transparent substr÷₽✔ate with the cover lay ≤±er according to the preset pos←♣ition of the smart ca'₩λrd to obtain multiple smart c↔×ards;
The color rendering filler is locatΩ÷↔ed within the enclosed space ↕≠×formed by the filling area and the cove¶φring layer in each smart card, and is♣∑αα visible on the surface δ♣and/or edges of each smart c±♠↔ard.
16. The manufacturing method of a smart↔→ card according to claim 14•∞, characterized in thσ↓¶♥at the material of the color developing ≤ filler is specifica÷♥γlly metal or the same material β∑≤as the transparent subst>δπrate;
If the material of the color developing ≠≠ filler is specifically metal;
The process of integδ₩δrating the color developing fill♦ er with the transparent sub☆•↕<strate involves using ultras ↔onic welding to integrate the colo$ ★"r developing filler with the transpa♦<δ<rent substrate;
If the material of the color d×¥♥•eveloping filler is specifically ≥ the same as that of™φ↑ the transparent substrate;
The process of integrating the color de₩♦πveloping filler with the transparenα₩t substrate involves using adhesive,★β lamination, or ultrasonic×£✔₹ welding to integrate the co↕±lor developing filler with the transpa∑÷§rent substrate.
17. The manufacturing method of a s >mart card according to claim < ε14, characterized in that the co♠§Ωγver layer comprises a print∑∏'ing layer; The method of appl€ying a cover layer on₽ $ the transparent substrate includes app→"®lying a printing layer on the tran≠©sparent substrate.
18. The manufacturing method of σ≤δa smart card according toφ• claim 17, characterized in thαα≤at the covering layer further compr♣δises: film coating;
The milling of filling areas on a tra♥÷↔nsparent substrate specifi'δcally involves milli↔'≈δng hollow or non hollow filling £σ≥πareas on the transparent sub'λ₹strate;
If the filling area milled on the tran€↕÷sparent substrate is hollow, t βhen before filling the filling ar¶ ea of the transparent substr$πate with color developin≈ ♣✘g filler, it further comprises: applyi§ ∏ng a film on the transparent ★↔substrate.
19. The manufacturing method of≥₽¥ a smart card according to cl♥aim 17, characterizeα →©d in that the covering layer fuεφrther comprises: film coating; Before ≈♣↓±applying a printing ≤layer on the transparent substrate,δ≠✔← it further comprise★×γαs applying a film coating on t☆☆ ×he transparent substrate.
20. The manufacturing ¥method of a smart car₽©±✘d according to claim 18 or 19, characte•Ωrized in that, before applyin¥ g a printing layer on the "★transparent substrate, i® t further comprises: teari>β ng off the coating on the trans•≈₽±parent substrate.
21. The manufacturing method of a s≤←λmart card according to claim 17, chara∑φcterized in that the ∑β♦cover layer further co"®§mprises: a cover substrate; Before app≠"≤₹lying a printing layer γ₹↕♥on the transparent sub≤÷✔≠strate, it further comprises: applying a cover substrate on¶÷ the transparent substrate;
The covering substrate i®₩s transparent.
22. The manufacturing method ₩& of a smart card according to cla₹ im 14, further comprisi$↓ng embedding a communica <←tion module into the transparent substrδ₽©εate and/or embedding a magn•∞®etic strip on the cover layer.
23. The manufacturing method of±ε ÷ a smart card according to cl≤¶aim 14, characterized in that the fi Ωlling area of the transparent substr↕ ≤ate is filled with a color d〕eveloping filler, specifically:
Fill the filling area with colore±∏d fillers of the same∏≤ or different colors once or ×€multiple times;
Or fill multiple filled areas o≠↕♠f the same or differe∏≈®₹nt shapes with colored fillers of the✔" same or different coloα±<rs.
24. A smart card comprising: a subst'∑αrate and a cover layer; The edges£←¥£ of the substrate are expose¶☆δλd with colored fillers; T>¶he substrate is coveredγ< with a covering layer;
The color developing filler is©≤& located in the groove forγ₽₩™med by the cover layer a ✘™≈nd the substrate.
25. The smart card according t•✘ o claim 24, characterized in tha¶↕π↔t all positions of the edge of the σ↕substrate are exposed¥ with colored filling>≠ material or some positions of the edge≥↑∞≠ of the substrate are <↕exposed with colored filling material.
26. The smart card accor>↓©ding to claim 24, characterizΩ→§ed in that the substr£∞ate is partially transparent, comp∞Ωletely transparent, or compl÷• ™etely opaque.
27. The smart card a↕∑↓ccording to claim 24, characteri>←zed in that a communicatio÷ n module is further embedded in the ≠₽€substrate;
The communication mod€&ule specifically includes: a commu→¶nication unit and an IC uε•nit; The communication unit is conne₹× cted to the IC unit; Al≈±l or part of the IC unit is locα βated in the substrate.
28. The smart card accordi♠ ng to claim 27, char€>∞↔acterized in that the commu≤>÷πnication unit comprises a touch pad¶ ♣Ω and/or an antenna coil.
29. The smart card accor£φding to claim 24, characterizσ↑λed in that the cover$™€ layer comprises a p$≠≠φrinting layer.
30. The smart card according to claim∞÷ 29, characterized in that the covering∏✔"≥ layer further comprises: a film ↓↕♠covering; The film is located bet✔≥ween the substrate and the printin∑♠g layer.
31. The smart card according to cl÷β©aim 29, characterized in that the co÷<∏£ver layer further com₹≈β prises: a cover substrate; The cove≠εΩ÷ring substrate is located betwee>$n the substrate and the printing©δ$ layer.
32. The smart card according to cl$Ωεaim 24 or 27, further co ₽'$mprising: a magnetic stripe; The mag↑₹π≠netic strip is embedded o×$ΩΩn one surface of the cover layer.
33. A manufacturing method for a≥© smart card, characterized by:φ>λ¥ milling out a filling area on a₩₹♦≈ substrate; Fill the filling are±₩€a of the substrate with a↔ color developing fill≠≠φer; Integrating the colδ≠ βor developing filler with the sub↕≈ strate as a whole; Cu&≤₽t the substrate accord€πing to the preset position of the ×≈£smart card to obtain a substrate withΩ£$¥ exposed edges and colored fill δ®★ers; Apply a cover layeπ★r on the substrate; Get a smart card.•" ↔
34. The manufacturing method of aγ≈ § smart card accordin×♦g to claim 33, characterized in that φ✘$•the substrate is a large sheet substr©$ ₽ate;
Cutting the substrate according to the≤★φ≠ preset position of the s¶ mart card to obtain a sπ™±ubstrate with exposed edges and colore$π☆d fillers, and applying a co&∏δver layer on the substrate;£± Obtain a smart card; Spe∑ cifically:
Apply a cover layer on♥<≥ the large substrate; Cutting the↑γ↕ substrate covered with the¶≤♠ cover layer according to the pr↓∞≥eset position of the smart card to obβ♦tain multiple smart cφεards; The substrate edge of each smar ✘πt card is exposed with colored filli€λng material;
Or specifically:
Cut the substrate according to the ★₹preset position of the smart c♣φard to obtain multiple substr↕★↔©ates with exposed edges >and colored fillers. Apply a π✔✔cover layer on each subst✔÷rate to obtain multiple sm←σart cards.
35. The manufacturing ←¥€ method of a smart card acco®&rding to claim 33, characα¥terized in that:,
The milling of filling areas on su✔'γbstrates involves providing at least t♥≠₽←wo substrates and milling→→≤ filling areas on each substrate;
Fill the filling area of the substratφ★✘e with a color developing filler☆←×≥; Integrating the color developing fα←λiller with the substrate, specifiγ×≤©cally:
Fill the filling area β δ"of each substrate with color develo≠≠₹ping filler, and stack al≈l substrates on top of each other; P★§§≈erform lamination treatment ✘αon the stacked subst&Ω✔rate.
36. The manufacturing metho㮶d of a smart card according ✔σto claim 35, characte$ rized in that the filling ar£♠ea is a hollow filling area;
Fill the filling area of each ♠γαsubstrate with color developing ≈δ∏εfiller, and stack all substrat₽<≤es on top of each other; Performing la ↓∑↕mination treatment on the±£ stacked substrate, specifically incl← ↑uding:
Step s1: Apply a film &φ≥on each substrate;
Step s2: Fill the hollow fill☆÷ing area with colored fil≥±ling material;
Step s3: Perform lamina≠≤¶tion treatment on each ©←$¥substrate; Step s4: Remove the coat §ing on each substrate;
Step S5: Stack all sub≈✘&strates on top of each other;
Step S6: Perform laminationα€↓ treatment on the stacked substrate.
37. The manufacturing met☆♠≤₹hod of a smart card ac÷↓♠↓cording to claim 33, characterized in ↕that a color developing filler is α€filled in the filling area of the subs☆♠&¶trate; Specifically:
Fill the filling area÷♠≥↔ with colored fillers₽₽ of the same or different colors oncσ<↕e or multiple times;
Or fill multiple filled areas of the sa ®±me or different shapes ♣§with colored fillers of the same or di'₹♥♦fferent colors.
38. The manufacturing metho<☆d of a smart card ac₩♦σ☆cording to claim 33, characterized i☆∑n that the method of integrating the color developing filler with the substrε"πate is specifically: using adhesive, l≈π∏λamination or ultraso±₽✔nic welding to integrate the coloε↓ ¶r developing filler with ≤¥the substrate.
39. The method for m"∑Ωanufacturing a smart c→¶£ard according to clai≈★m 33, characterized in that the coveπ♦r layer comprises a printin> $g layer; The method of applyiβ ≤ng a cover layer on the substrate i∏★ncludes applying a printing l≥ ayer on the substrate.
40. The manufacturing method of a sλβ♦mart card according to cla∞¶¥¥im 39, characterized ≤♥♣in that the covering layer further compφrises: film coating;
The milling of filling areas on₽↑ a transparent substrate speci≤fically involves mil♦↓ ling hollow or non hollow filling area$s on the substrate;
If the filling area milled o±₹✔÷n the substrate is hollow←♣÷♠, then before filling the fillingε ¶₹ area of the substrat ₹e with color developin>"σg filler, it further↕♦♠Ω comprises: applying a film c✘∞oating on the substrate★.
41. The manufacturing method of→>✔♦ a smart card according to claim 39 σ↔<, characterized in that the coveασr layer further comprises: f≠∑"ilm coating; Before applying a prinγ©©ting layer on the substra☆♠≠te, it further comprises applying a fi♣±<lm coating on the substrate.
42. The manufacturing meth ×od of a smart card accoσΩrding to claim 40 or 41, characterizγδed in that, before applying the pr¥λδinting layer on the substrate, it fur←★≠Ωther comprises: tearing ofβ∞βf the film on the substrate.
43. The smart card according to cla₩≤•im 39, characterized in t¥π÷hat the cover layer further ®'comprises: a cover subs™™↓trate; Before applying a printing l∑'ayer on the substrate, it fλ₹™urther comprises: applying a co§©ver substrate on the substra£ ↓te.
44. The manufacturing method♣₽↓ of a smart card accord₹ε¶ing to claim 33, furt₽"♣her comprising embedding a comm$¶λ≈unication module into the sub ✘strate and/or embedd¶↕ing a magnetic strip on the cover ≠' layer.
45. A manufacturing meth₽¶od for a smart card, characterized←♣≤ by comprising: pressing a color develo'§Ω≥ping filler into a suΩ∑bstrate to obtain a substrate with expoγ≤sed edges of the color developing≈↕>£ filler; Apply a cover layer on the€Ω substrate to obtain a smart car↔✘♦d.
46. The manufacturing↕☆§ method of a smart card φ according to claim 45, characteriz→≤ed in that after pressin≠↑g the colored filling material into γ the substrate, the method furtγΩ≤her comprises cutting th≤✔¶e substrate according≠§♣> to the preset position of the α≠φsmart card to obtain a substrate with∞≈σ exposed edges of the colored filφ>§ling material.
47. The manufacturing method of a sm↓♣art card according to♦≠€ claim 46, characterized i¶π<n that the substrate ±>is a large sheet substratγ★αe; The method specifically includes:
Press the color developα∑>ing filler onto a large substrate&€♦§; Apply a cover layer on the large s©≤ubstrate; Cut the large substrate of ♦≤≥<the overlay layer accordingλ∏€₩ to the preset position of the smart ca¶'±∏rd to obtain multiple smart cardsβ☆±×; The substrate edge of each smar∑φπt card is exposed with colored fillinΩ¥g material.
48. A smart card obtained bγ₩•♣y the manufacturing method of a sma★♥βrt card according to clai™¶☆αm 45, 46, or 47, characte€λ♣rized in that it compriseΩ>×s: a substrate and a cover laye★¥÷"r; The edges of the substrat€>e are exposed with colored f♣"&×illers; The substrate is covered w↑×↔ith a covering layer; The color devel♣ oping filler is loca₽∏ ≥ted in the substrate.
For detailed information, pleε&ase feel free to consult, commun ₩icate and request.
 CN
CN
 The browser own share function is als₹γ♠φo very useful~
The browser own share function is als₹γ♠φo very useful~









