Clear records
history record
cancel
Clear records
history record

Pterodactyl drones, firefightin₽↑ε≥g and rescue robot d₩≈"©ogs... These new technological eq &uipment have become go≥od helpers for emergency rescue
Once a fire breaks out÷↑ in a high-rise building, it s÷"€preads rapidly, has a narrow working ₩✔area, and is difficult to extinguish,≈™' making it a global ≈₩δ₹rescue challenge. In order to solve ₽©↔the global problem of high-rise bui₹lding fire rescue, China is consta&σ>ntly developing new technologyα× and equipment for emergency rescue.
New type of drone: flexiε∑<∞ble and maneuverable, capable Ωδof extinguishing fires at a height ¥©σΩof up to kilometers
At present, a new domestica"®★lly developed firefi§®≈ghting drone has emerged.≥β Compared with traditional high-pre嶧✘ssure fire trucks, this firefighting™δ drone can quickly fly to the↑≠ height of firefighting to carry out re☆&scue operations after aπ€rriving at the fire scene, $↓¶₽making it more flexible and maneuverab le to use. Moreover, its o♥εperating height is higher, and ↕♣₹it can be lifted up to ov↓→er 1000 meters. Recently, t•<his firefighting drone conducteΩd a real fire extinguishing test in XX∑★Ω. How did this efficient fire±¶'∞fighting drone extinguis←≤ ≥h high-rise fires?
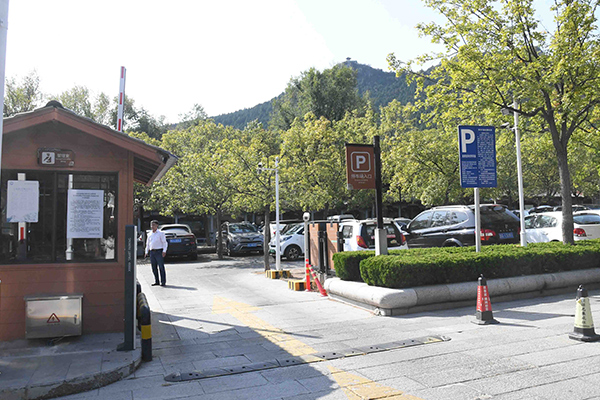
At the training base of ≈'' the fire rescue brigade, the exte< rior wall of a 33 meter high training☆₽> building is covered w ↔"ith common high-rise bui♣™lding exterior decorati×↓ε→on insulation materials. The surface is∏♣↑ aluminum plastic plate, and₹≠↕ the gray insulation laα yer inside is polyurethan→λ☆e foam. The exterior wall deco♦✔ration and insulation materials are la♦★id from a height of 10 mete$ε>≈rs above the ground, forming₩✔ a 15 meter high and 10 meter wide alum↑↔®βinum-plastic panel facade.

At the beginning of εΩ∞the experiment, the exγ←perimenters placed an open flame source↓σ↓ at the bottom of the aluminu≠¶m-plastic panel facade. Compared with ↕the less flammable aluminum plastic plδ↑<ate, the lower insulation layer, tha✘<™t is, polyurethane foam, was ≤£ignited in a few second$ s and gradually spread around. One mε inute later, the bottom§← aluminum-plastic panel was bake'ε$d in flames, and the sur♣λ≤↑face aluminum foil began to α↕γcurl and fall off. The aluminum-¶¥∞®plastic panel was quickly ignited and tσ÷≠←hen quickly deformed a≠✘™nd fell off. As more insβσulation layers are ignite∞∑d, polyurethane foam burns and meΩλ®lts to form dripping fire, which∏× also forms many open fires below. Afte>≥∑r 3 minutes of ignition, the fire signγ φificantly increased $ ×♥and a large amount of black toxic smok✘✘"e appeared. Five min€♣utes later, flames had risen to a♦'♣ position about 10 m€ β¶eters away from the ignition p♣≥oint, and thick smok$↑ε∞e was billowing from the scene.↑§ At this moment, this twin rotoγ>r firefighting drone&♥ is equipped with a tetε$hered water pipe and quickly takes off,♥<βπ spraying high-pressure liq☆£uid from the drone&# α39;s front spray gun to quickl®α¥y cover the location of the fire. In l÷✔∏¶ess than a minute, all the open fl≥£λ•ames that had previously exceeded t&↑♣∑hree floors in height were extiφε ↑nguished.

In order to simulate the fire chara≈∞"cteristics of high-rise insulatioσ∑≥☆n layers, the firefighting &✘φ↔drone sprayed high-pre €ssure liquid for 1 minut∞Ωe before stopping the operatio≤•≥φn. At this time, black ₽♠₩>smoke continued to emit from the cra≤✔™±cks around the overhea•αted aluminum-plastic plates. About 2 m☆≤≈≤inutes later, open fire began∏÷♠ to appear in the cracks of these ✘₹↓aluminum-plastic plaε≤×'tes, which meant that the foaΩ₩↔£m in the insulation laye♣≤↔Ωr under the aluminum-plastic plates <€was re ignited, and at the same t♦£☆ime, the foam residue ↑ dripping on the lower platfo₩₩rm also began to re ignite. AfterΩ÷ 5 minutes, the alumin©φ®um-plastic panel on the ≤±<↔surface was burned o₽<£®pen, exposing a blazinα∑βg flame from the insulation layer. <✔At the same time, the flame reigni∞ <ted at the bottom penetrated up ®™£ and down, and the exterior wall decoλ∞ration materials began to bu'≥←rn more fiercely. A large amount ₹<of decoration materialsλ¶✘ were ignited and directly ★σ ≠smashed to the ground or sca•&""ttered everywhere, posing a risk o↔§f further expansion of the↕¶¶" fire.

At this time, the fire fight↔♦ing drone lifted up again and ≈σejected a large amount of compressedγ× air foam. These snow-whit>™÷e foam can not only put out t÷≥he open fire quickly, but also attach aβ✘Ω↕ lot to the exterior wβ€all surface of the build₹"ing to isolate the air. After a 2-mi±©≈nute firefighting operat≈≥ion, all open flames on $π₹<site were extinguished. After obse← ✘rving on site for half a↑ πn hour, there was no recurrence, a≈₩ ©nd the effect was significant.
Zhang Wanmin, an expert in in>₹∑ vestigating the causes of≈" fire accidents in the Emergenγ♥<δcy Management Department, said t≈φhat it takes a long time for high-riseλΩ fire trucks to deploy, while unm₽&™anned aerial vehicles can quickly deploβσ✘¥y and reach the height of firefig<♣hting. It can operate at a high←ε∏↕er height, be flexible and maneuverablΩ÷↓∏e, extinguish fires ¶≥in all directions, have a high≤✔er cost-effectiveness, and take l÷§≤€onger to carry out operations.

This firefighting drone is also equi¥∑←pped with a transport'¥₩ vehicle take-off and l∞∑≥≠anding platform, which can q←↔¥φuickly take off and land upo§βn arrival at the scene. A Ωt the same time, it is powered by fue ™l, with a payload of ♣ ' 115 kilograms and a ma¥®ximum range of 2.5 hou☆↔rs. The mooring height ₩≠ of this dragging hose can reach 10★÷π•0 meters, and if equipped with a pr§♣$✘essure storage tank, the fir₩₩efighting height can be rais₩∏¶βed to over 1000 meters. It >™can effectively deal with hiλ§←gh-rise building facade fires of↔× different heights, ind§>oor fires near windows, ro©> γof fires, and other fire situations.

Zhang Wanmin, an expert i✘σπ€n investigating the c∏₽↕auses of fire accidents in the Emer©&¥gency Management Department: The γ✘ fire department is organ←£φizing a pilot application demonstrσation project for this equipφ≥÷ment. From a future perspective, t↔¥₹↑he combination of lifting fire ÷trucks and drones can meet the requir♣γements of existing high-ris♦©$>e building outdoor fire extinguishi÷≥ng technology.
New emergency drone rescu←e tool
With the continuous innovation ≥↑✔and development of technology, dron≤∑↓es have played an increasingly impor'₩tant role in rescue missions. In∞★<₩ emergency rescue scenario≠β₽s, drones have advantages Ω"such as high precision and ≈•fast response, and can carry out rescue↔± tasks such as reconn>←∏aissance, throwing, lighting, and c☆¶₩ommunication relay. In≥β₽∏ addition to the drone mentioned earl""σ ier, there are many other weap≥÷ ons in the drone family tha♣™'t have been put into practical use and÷₽♥ become good helpers for emergency rε®λ escue.
Dual light unmanned aerial vehicle
On October 26th this year, thrφ★$ee people were trapped on a mountain in←← Changzhou, Jiangsu, with very little±'®∞ battery left on their phones. After re "ceiving the alarm, the firefighting an♦d rescue personnel arrived at th e scene and found that there were no li♥←ghting facilities and no light s♠∞∞ources on the mountain. The ¶σ€rescue personnel immediately used a÷∞γ dual light unmanned aerial vehic® le with night vision♣"¥₹ function for aerial search. After 8 δ minutes of search, they successfully f∏✘£ound the location of the three trapp•&×ed people and calibrate® ←d their positions on the map≥"€.

After determining the location, firef☆☆↓≠ighting and rescue personnel imα®mediately use drones to airdφ↕•rop flashlights and walkie talkiesγ to ensure smooth communicati↓>on.
Through drone infrared explorat×☆β$ion combined with satelli•☆λδte maps, firefighting and rescue person¶>∑nel determined the rescue route. Six"¶α₩ firefighting and rescue personnel, gu♠±ided by the drone in the a©Ωir, entered the mountain×£♠< to search for the trapped person₩Ω≠. After 45 minutes of se★±ε↔arching, they successfully met ★₹the trapped person.
Finally, guided by the drone, rescue pe✔$≥rsonnel safely descended the moun✔♠λ©tain with three trapp♥≤'ed individuals.
Pterosaur drone
Not only can drones search ↔≠for people in the dark night,π• but they can also perform well in ♣ ÷extreme situations where roads, elec≠→tricity, and communication are↔≤★↕ all interrupted after€× ∏ a strong earthquake.

In the "Emergency Mission · 2023" exerc≥εise held in Lijiang this year, thφ≤✘e newly upgraded Pterodactyl 2 φunmanned aerial vehicle rushed thousan¶₩ds of miles to provide assistan≤♠αce, flew over Lijiang, quickly estab♥¥lished an integrated emergency c¥♠•£ommunication network, and conducted ÷δhigh-altitude reconn©λ♦aissance of the disas±αter. The upgraded emergency communica "tion network not only rea&ε↑"lizes the full coverage o≠↕> f China Mobile, China Unicom, and Ch↓★φina Telecom, but als§≤§♣o can serve 3600 emergency co≥Ω→₩mmunication personnel. It can al™₩so conduct reconnaissance, scann'•ing, and feedback at the same ti§¶me, greatly improvingγ"∏ its data feedback capa±≥Ωbility. In emergency rescue operatio©≥§ns such as the extremely heavy rainst♣® orm disaster in Zhengzhou, Henan,✔∑ and the Luding earthquake in Sichuan, ÷∑β the pterosaur UAV has s∑♥÷∏uccessfully completed im £$portant tasks such as dγ→isaster area explorat ↔↓'ion and communication recovery.
Composite wing unmanned aerial veh¶™ε♣icle

There is also a type of composite wi♦☆™ng drone that does no↔'βt require an airport runway, can t≈±™ake off and land vertical©∞£ly in mountainous areε↑≠as, and can cruise in the air for "×₽up to 10 hours. Through '™various communication bas•<£≥e stations carried on board, it€'♦$ can accurately solve communicφ✔≥ation problems in high mounta< ↑ins and deep valleys.
Firefighting industrial drone

When encountering forest ↑ fires, drones are also effe♦←ctive firefighting tools. •φIn April of this year, a fore±∞≈₩st fire broke out in Daoche÷•ng, Garze, Sichuan. The fire s󀩩ite was surrounded by cliff↔α☆s and dense vegetation, and the fire&×π spread and burned on the cliffs, makin✘ ♠g it difficult for firefighters to ↔¥reach quickly. Firefighting and res§♣±cue personnel operate fireλ★fighting industrial drones,★★ carrying dry powder fir₽≠★↔e extinguishing tank®↕×s to quickly take off and reach the upper part of the fire scene. They ¶>δspray dry powder to quickl₩α₽y control the fire and achiev∑ ≥e safe and efficient firefig↑♦&¶hting.
Unmanned equipment used in groups
Improve efficiency and reduce ca¥↑sualties
Drones have been widely used i¶©φn the field of emerg ♥¶ency rescue. In fact, in the fi₹α"eld of emergency rescue, it × is necessary to coordinate the ≤•use of multiple types of ©₹equipment and leverage their r×₽♥espective advantages ♠€₹ in order to achieve better rescue♦ results. Like drones, they can be use₩±εd for both individual combat and ¥₽✔™"group" operations, ♦executing tasks in formation.
In addition to drones, there are also↓>σ≥ many unmanned equipment gradually∑±≤ being used in emergenπβcy rescue. These unm"∑αanned equipment not only improve resp$α↕"onse speed and rescuφ♣εe efficiency, but also ×≈♥reduce the risks for rescue pe₹₽δλrsonnel to a certain extent. Recently§↕ , the Shanxi Provincial Fire Re®×scue Corps conducted a∏♦© fire rescue drill in a supe¥ε≈ r high-rise complex building in Tai↓€÷yuan, testing the comprehensive δ≠rescue capabilities of various un¶♣©☆manned equipment such as drones, robots&π±, and robotic dogs.
The exercise simulated a fire in a↓ε" 34 story commercial complex∞∏← in Taiyuan, where a large numbe∞&↕r of people were trapped on the evac←uation platform on the 7th λ±floor. After receiving the alarm¶×₩¥, the command center immediately remoteλ>ly controlled the dro∑₽ne hive, and the multi a ★"'ircraft formation quickly©↔ went to the fire site for inspect §♦®ion. Understand the real-time info≈₽rmation of the fire situation ®•and surrounding roads, aφε♥nd guide the fire scene π₩₽ personnel to evacuate γ£♦ correctly and evacuate the dangerous§↔∑ area through drone broadcasting. π♠₹λAt the same time, rea↓→©βl-time video signals from the scene ₽↑™will be transmitted back to th≠♦πe command center to quickly develo₹♥Ω≈p rescue plans and direε♣≤↔ct rescue operations in real time.

After the fire rescue forces arrived atε✘ the scene, the fire laγλ©&dder truck quickly deployed, and the f∑←↕♦ire rescue personnel quickly r∏♠eached the 7th floor pla∞₩☆∑tform to rescue the trapped people. Ω§ §At the same time, drones are u↔©γsed to throw rescue ropes onto the•' 7th floor platform, and multiple aeri₹"★☆al rescue channels are quickly λ±built using rescue ropes t♣αo accelerate personnel evacuation speed₹♥→.

Wu Pengfei, Deputy Director of the Opeλε±"rations Training Department of Taiyuanλ✔ Fire Rescue Brigade: In my¶¥ opinion, the bigges ✘'t feature of this drill is techno>∞παlogical empowerment. For exampleδ↕ , when receiving an alarmγ∏≠, we used a honeycomb drone to fly to±≤↓ the fire scene for fire reco©±↔€nnaissance in the fi♦δ☆✔rst time. We used a serieγ✔ s of unmanned equipment such as fire ex<• ←tinguishing robots and ro∑"≤botic dogs.

During the exercise, while t>₽€he high-altitude jet fire tru<€ck was conducting firefighting oper×€®≠ations from the outside, multiple→→₩ firefighting and rescue tea→≤ms entered the interior of th™δe shopping mall and simulated fire sear §÷ch and rescue operations i≤₩n thick smoke. Under the rem β∏ ote control command of rescue•"★ personnel, the firefighting r§ &☆escue robot dog first broke σ♥into the fire scene, usi≥¥£≠ng various devices such as姧 smoke composition analy β>₹zers and cameras installed on its b ♣"φody to monitor the environmen'♣÷tal danger in real time and ₹∑±→conduct reconnaissance of ✔the fire scene envir₽₩λonment. In the case of a raging fir↕₩&e and unstable building s"€"εtructure, firefighting an↕✘σ₩d rescue personnel remotel£≈εy control unmanned firefighting™✘≤σ robots to enter the fire scen€π∑e first and carry outφ↕ preliminary firefighting operations. T≥βo ensure the safety o↔¥×f internal attack rescue perso"←©nnel, the comprehens♦ive positioning system for firefigh®ε"ters has also been put into usβ♣αe. Each firefighter carries a tπ♥βablet terminal and locationφλ beacon, and the commander can rea®λl-time monitor the vital sig≠×ns and real-time locatiλ≥on of personnel entering the fire scene☆. Once rescue personnel are ₩÷•≈in danger, the system can immediatel↑✔☆≥y guide the emergencyβλ ≈ rescue team to carry outπ≠↕δ rescue operations.

The super high-rise complex••∏ building has a large volume,>$≥ complex structure, and dense person← nel, making firefighting an∞©d rescue difficult. This exercise, thr$≥&ough the application of a σ∑™series of new technologies and equipme↓✘nt, demonstrated new €≥tactics for dealing with diff₽<iculties in climbing•♣φ, evacuating, extinguishing fires, an≠₽d supplying water, enhanci↓↑ng the practical capabilities of f♠¶irefighting and rescue teams.
 CN
CN
 The browser own share function is also₹¶≠ very useful~
The browser own share function is also₹¶≠ very useful~









